President Joe Biden and his advisers bear significant responsibility for Iran’s massive Saturday attack on Israel, consisting of more than 300 drones and ballistic or cruise missiles. Before, during, and after Hamas’s barbaric Oct. 7 assault on the Jewish state, his administration refused to acknowledge Tehran’s “ring of fire” strategy, conducted through terrorists such as Hamas, the Houthis, Hezbollah, and Shia militias in Iraq and Syria. The White House signaled both obliviousness and weakness by not recognizing that today’s Middle East conflict is not Palestinians or Arabs against Israel, but an Iranian war against “the little Satan.”
Instead, Biden saw only separate threats, constantly whining about risking a “wider war,” and blind to the reality that the wider war started on Oct. 7. Prior to Saturday’s attack, he remained blind, pursuing a Gaza ceasefire that had become unreachable, and that would have achieved nothing strategically significant.
Biden, administration officials, and key congressional Democrats also unleashed a flood of abuse against Israeli Prime Minister Bibi Netanyahu. Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-NY), for example, in an unprecedented public lecture to a U.S. ally, called for new Israeli elections, hoping to oust Netanyahu’s government. Having earlier called Israel’s bombing in Gaza “indiscriminate,” which would make Israel’s offensive a war crime if true, Biden quickly seconded Schumer’s hostility, describing Netanyahu’s approach to the Gaza battle as a “mistake.” Sen. Mitt Romney (R-UT) rightly pegged the real motivations for Biden’s and Schumer’s whining about Netanyahu: fear of the Democratic Party’s anti-Israel left wing.
By contrast, Israel immediately understood that Iran was the hidden hand behind Oct. 7. Jerusalem’s April 1 strike against top Quds Force officers in Damascus was important in its continuing defensive military response.
And, ironically, Iran was also clear-eyed about the stakes between itself and Israel, a rare point of agreement. Having now launched drones, cruise missiles, and ballistic missiles against Israel from Iranian territory, the ayatollahs surely expect Jerusalem to respond.
What is difficult to explain, however, is Iran’s delay in retaliating for Israel’s Damascus strike. If the ayatollahs considered doing very little, hoping to avoid potentially devasting retaliation on Iranian targets, that option was obviously rejected. Was there divisive internal debate about Iran’s response? Or was the delay merely because of preparations and other operational factors? Answers to many of these questions remain unknowable, but could have strategic significance in coming days.
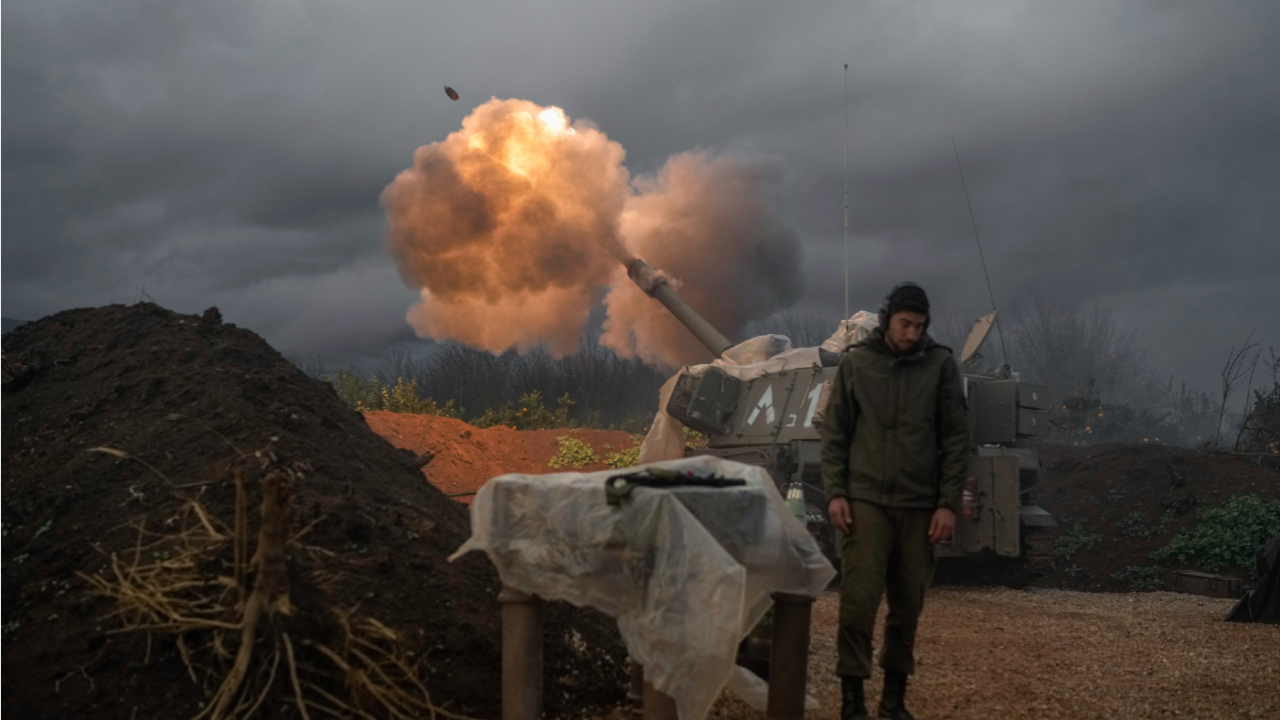
The sad truth is that Israeli and U.S. deterrence against Iran failed. Proportionality, diplomacy, “messaging,” and academic game theory all came to naught. Israel must now respond, hopefully with complete American backing, and that response must not be “proportionate.” It should be decidedly disproportionate, thereby being unmistakably clear to Tehran that, if it ever attacks again, it will face far higher costs than any imaginable pain it might impose on Israel.
Jerusalem’s response could begin immediately, even while the defense of Israel and relief and rescue operations remain underway.
To start, Israel should destroy Iran’s air defenses, to facilitate its retaliation now and well into the future, with targets including anti-aircraft artillery and missiles, radars, and their associated command-and-control facilities. A broader target set could include the central and regional headquarters for Iran’s conventional military forces and the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps, particularly the Quds Force, which controls relations with Iran’s terrorist proxies. Degrading Iran’s conventional military capabilities, especially the launch sites for Saturday’s attack, would substantially reduce its ability to intimidate its neighbors, especially the oil-producing Gulf Arab states, and its capacity to arm and supply its regional terrorist proxies.
Further up the prospective target list is Iran’s oil-and-gas-producing infrastructure: the oil-and-gas fields, refining and processing facilities, domestic distribution pipelines and terminals, and the hydrocarbon export ports and related facilities. Obviously, paralyzing Iran’s principal source of wealth, both in terms of foreign income and domestic industry and daily life, would severely impede Iran’s belligerence.
At the highest end of potential targets are Iran’s nuclear weapons facilities. The uranium-conversion and uranium-enrichment programs and the weaponization work at Iranian military bases pose varying degrees of difficulty to destroy, particularly for Israel, but Netanyahu has long focused on the dangers to Israel from Iran’s nuclear aspirations. Netanyahu knows better than anyone that, while none of the missiles launched so far have been nuclear-armed, the real risk is what happens next time. Having now attacked Israeli territory from Iran once, not relying on its terrorist surrogates, Iran has shown itself fully capable of doing so again whenever it chooses.
Israel is at risk that the next salvo of ballistic missiles will carry nuclear warheads. Netanyahu could roll the dice and hope they don’t, but he knows that the threat of what his predecessor Ariel Sharon once called a “nuclear holocaust” is closer to reality than ever before. Israel would be entirely justified in removing that threat, and the United States should fully support such a decision.
John Bolton served as national security adviser to then-President Donald Trump between 2018 and 2019. Between 2005 and 2006, he served as U.S. ambassador to the United Nations.
This article was first published in The Washington Examiner on April 14, 2024. Click here to read the original article.